CIL and JIT
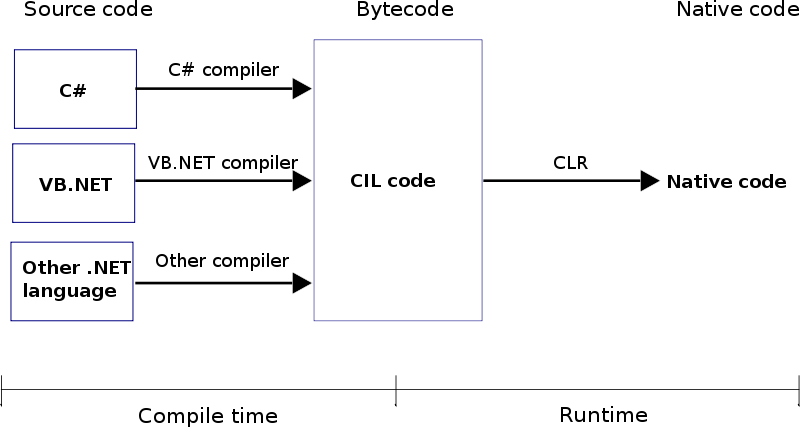
When you compile code that uses the .NET Framework library, you don't immediately create operating-system-specific native code. Instead, you compile your code into Common Intermediate Language(CIL) code. This code isn't specific to any operating system and isn't specific to C#.
Obviously, more work is necessary to execute an application. That is the job of a just-in-time(JIT) compiler, which compiles CIL into native code that is specific to the OS and machine architecture being targeted. Only at this point can the OS execute the applications.
Assemblies
When you compile an application, the CIL code created is stored in an assembly. Assemblies include both executable application files that you can run directly from Windows without the need for any other programs and libraries(which have a .dll extension) for use by other applications.
In additoin to containing CIL, assemblies also include meta information(that is, information about the information contained in the assembly, also known as metadata) and optional resources(adition data used by the CIL, such as sound files and pictures.) The meta information enables assemblies to the fully self-descriptive. This means that deploying applications is often as simple as copying the files into a directory on a remote computer.
CLR
The Common Language Runtime (CLR) is the virtual machine component of Microsoft's .NET framework and is responsible for managing the execution of .NET programs. The native code is executed in the context of the managed CLR, along with any other running applications or processes.
When you compile code that uses the .NET Framework library, you don't immediately create operating-system-specific native code. Instead, you compile your code into Common Intermediate Language(CIL) code. This code isn't specific to any operating system and isn't specific to C#.
Obviously, more work is necessary to execute an application. That is the job of a just-in-time(JIT) compiler, which compiles CIL into native code that is specific to the OS and machine architecture being targeted. Only at this point can the OS execute the applications.
Assemblies
When you compile an application, the CIL code created is stored in an assembly. Assemblies include both executable application files that you can run directly from Windows without the need for any other programs and libraries(which have a .dll extension) for use by other applications.
In additoin to containing CIL, assemblies also include meta information(that is, information about the information contained in the assembly, also known as metadata) and optional resources(adition data used by the CIL, such as sound files and pictures.) The meta information enables assemblies to the fully self-descriptive. This means that deploying applications is often as simple as copying the files into a directory on a remote computer.
CLR
The Common Language Runtime (CLR) is the virtual machine component of Microsoft's .NET framework and is responsible for managing the execution of .NET programs. The native code is executed in the context of the managed CLR, along with any other running applications or processes.
Comments
Post a Comment